
At the dawn of the nuclear age, the United States hoped to maintain a monopoly on its new weapon. The atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945 marked the beginning of a nuclear arms race. The Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, France, and China joined the ranks of nuclear powers in the following two decades.

Attempts to curb the spread of these apocalyptic weapons led to the nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT) in 1968, but not all were deterred. India, Israel, and Pakistan never signed the NPT and possess nuclear arsenals.

Iraq initiated a secret nuclear program under Saddam Hussein before the 1991 Persian Gulf War.

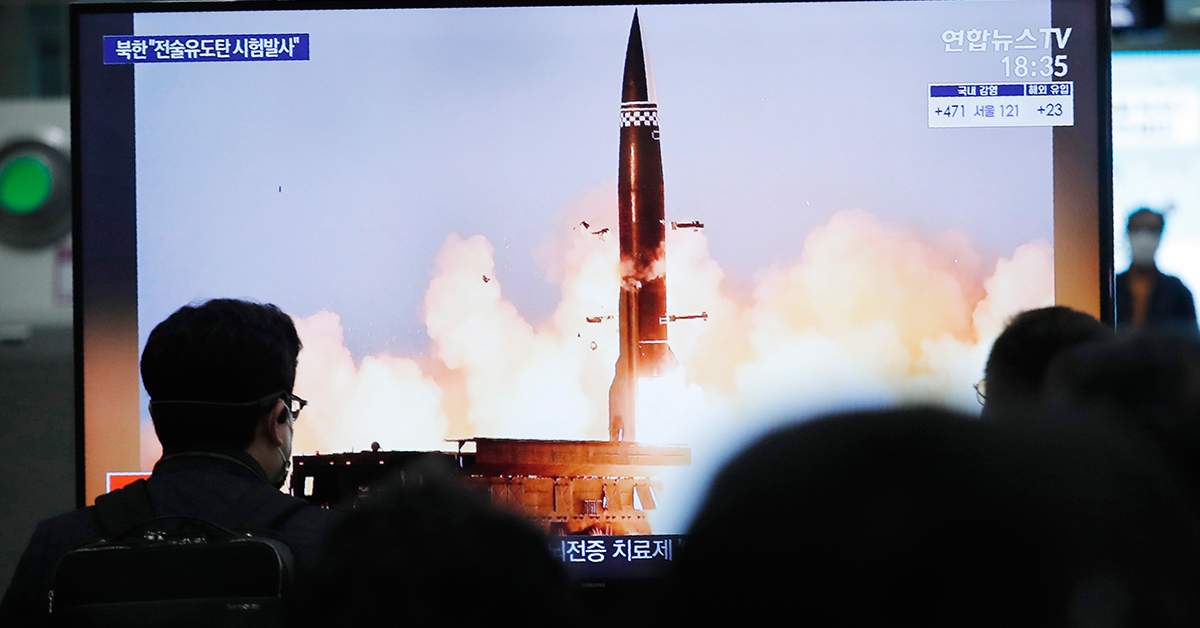
North Korea announced its withdrawal from the NPT in January 2003 and has successfully tested advanced nuclear devices since that time.
Iran and Libya have pursued secret nuclear activities in violation of the treaty’s terms, and Syria is suspected of having done the same.

While nuclear stockpiles have been reduced significantly from Cold War heights, nine countries now command roughly 12,100 warheads, with the United States and Russia holding 88% of these.

Notably, Russia suspended its participation in the New START Treaty on February 21, 2023, However, both the U.S. and Russia have committed to the treaty’s central limits on strategic force deployments until 2026.

The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) estimates that Russia’s military stockpile consists of approximately 4,489 nuclear warheads, with 1,400 additional retired warheads awaiting dismantlement, as of May 2023.

FAS estimates the U.S. current military stockpile stands at 3708 warheads, with 1,536 retired warheads awaiting dismantlement, for a total of 5,244 warheads as of early 2023.

As of October 2023, the Defense Department assessed that China has a total of 500 nuclear weapons and, if it remains on its current trajectory, may have up to 1000 deliverable nuclear warheads by 2030.

France has a military stockpile of 290 operational warheads available for deployment on 98 strategic delivery systems, as of January 2022.

As of January 2022, the United Kingdom has a military stockpile of 225 warheads, of which an estimated 120 are operationally available for deployment on 48 submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and 105 are in storage.

Non-NPT nuclear states have smaller but significant arsenals. India is believed to possess up to 164 nuclear warheads, Pakistan around 170, and Israel an estimated 90. North Korea, despite its tumultuous relationship with the NPT, is estimated to have 30 nuclear weapons and continues its pursuits.
Iran has accumulated enough uranium enriched to 60 percent to build a nuclear weapon, but the warhead would be large, unwieldy, and inconsistent with the weapons-related work Iran did prior to 2003. Iran has not accumulated or enriched uranium to weapons-grade levels (90 percent).

On May 8, 2018, President Trump announced that the United States would withdraw from the JCPOA. Iran began to violate the accord a year later. The United States and Iran have not yet reached an interim agreement to replace the JCPOA.
Relevant articles:
– Nuclear Weapons: Who Has What at a Glance, Arms Control Association
– Status of World Nuclear Forces, Federation of American Scientists
– Nuclear Weapons Worldwide, Union of Concerned Scientists
– NMHB 2020 [Revised], OUSD(A&S) (.mil)

